Tabs
Within the configuration of each item, there are several tabs when creating a new service plan item, below is a summary of these tabs.
General Tab
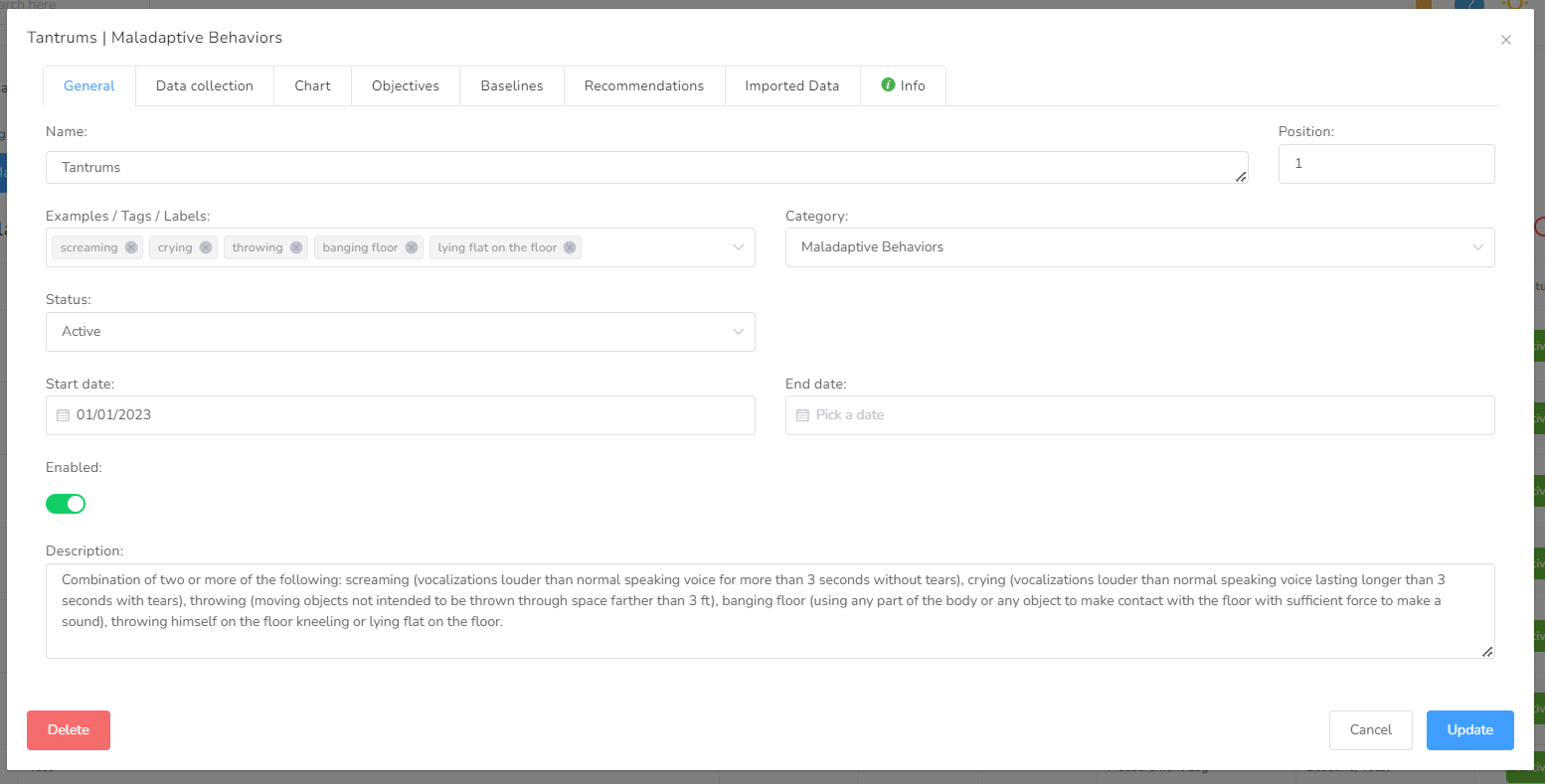
- Name – The actual name of the element of the service plan.
- Position – Position of the element inside the service plan.
- Examples / Tags / Labels
- Category – The category, to which this service plan belongs, is useful if it needs to be changed.
- Status – Defines the status of the category: Active, Hold, Monitoring, Maintenance, Discontinued, Met.
- Start date – The initial date associated with this element is useful to determine the first day data will be collected or displayed inside a document.
- End date – The last date associated with this element is useful to determine the last day data will be collected or displayed inside a document.
- Enabled – If this element is active or not. Useful also prevents the element to appear in other places.
- Description – Longer definition of the element, typically a full narrative description.
Data Collection Tab
We have implemented more than 15 data collection methods, please refer to the following table for more details.
| Type | Description | Methods |
| Event Recording | The number of occurrences by a unit of time. Ex: hour, day, week, interval. | Frequency, Count, Rate |
| Time Sampling | Collect data at periodic points in time or time periods rather than on a consistent basis. | Whole Interval, Partial Interval, Momentary Time Sampling |
| Timing | Length of time the behavior, or event occurred. | Duration, Response Latency, Interresponse Time |
| Trial | Several ways to easily record whether a response has been Correct, Incorrect, or there was no response to the test applied. | Discrete Trial Teaching, Incident Teaching, Percentage of Opportunities |
| Task analysis | Task analysis is used to break complex tasks into a sequence of smaller steps or actions. | Forward Chaining, Backward Chaining, Total Task Chaining, Backward Chaining with Leaps Ahead |
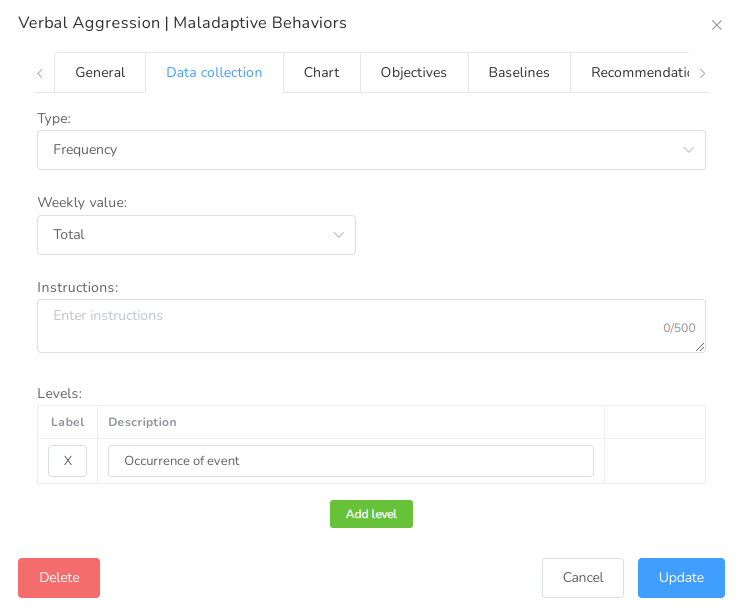
- Suggested number of recordings – Expected number of recordings for this element of the service plan. It is a suggestion, so they could go over this number.
- Daily Value – Value calculated for the day, possible choices are: Total or Average.
- Weekly Value – Value calculated for the week, possible choices are: Total or Average.
- Instructions – These instructions notes are given for the user collecting the data, this will be displayed in the datasheet.
- Unit of time – Determines the unit of time of the recording
- Interval Length – Used for interval base collection methods to determine the interval length (in the unit of time)
- Levels – If you would like to personalize the levels of data, you can do so by adding different Labels that will become the legend used.
Charts Tab
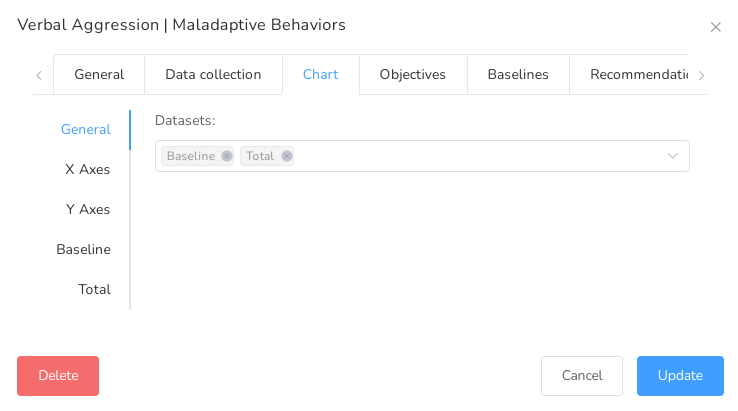
List of some of the datasets to be displayed in the chart.
| Dataset | Description |
| Baseline | Expected behavior of data, used for comparative purposes. |
| Average | Average of values through a day, week, month, or year. |
| Total | The total value of data during a day, week, month, or year. |
| Rate | Occurrence of an event during a unit of time. |
| Count | The total value of data collected. |
| Session count | Count of sessions during a day, week, month, or year. |
Other features available such as:
- Show multiple datasets at the same time on the same chart.
- Customize X and Y axis (Title, Position, Font size, Label rotation, Max value, Min value, Step Size, etc.).
- Customize each dataset (Title, Associated axis, Type, Point Style, Colors, etc.).
- Show ignored dates and values.
- Show the data in daily, weekly, monthly, or yearly intervals.
Check Chart’s Configuration article for extended information about it.
Objectives Tab
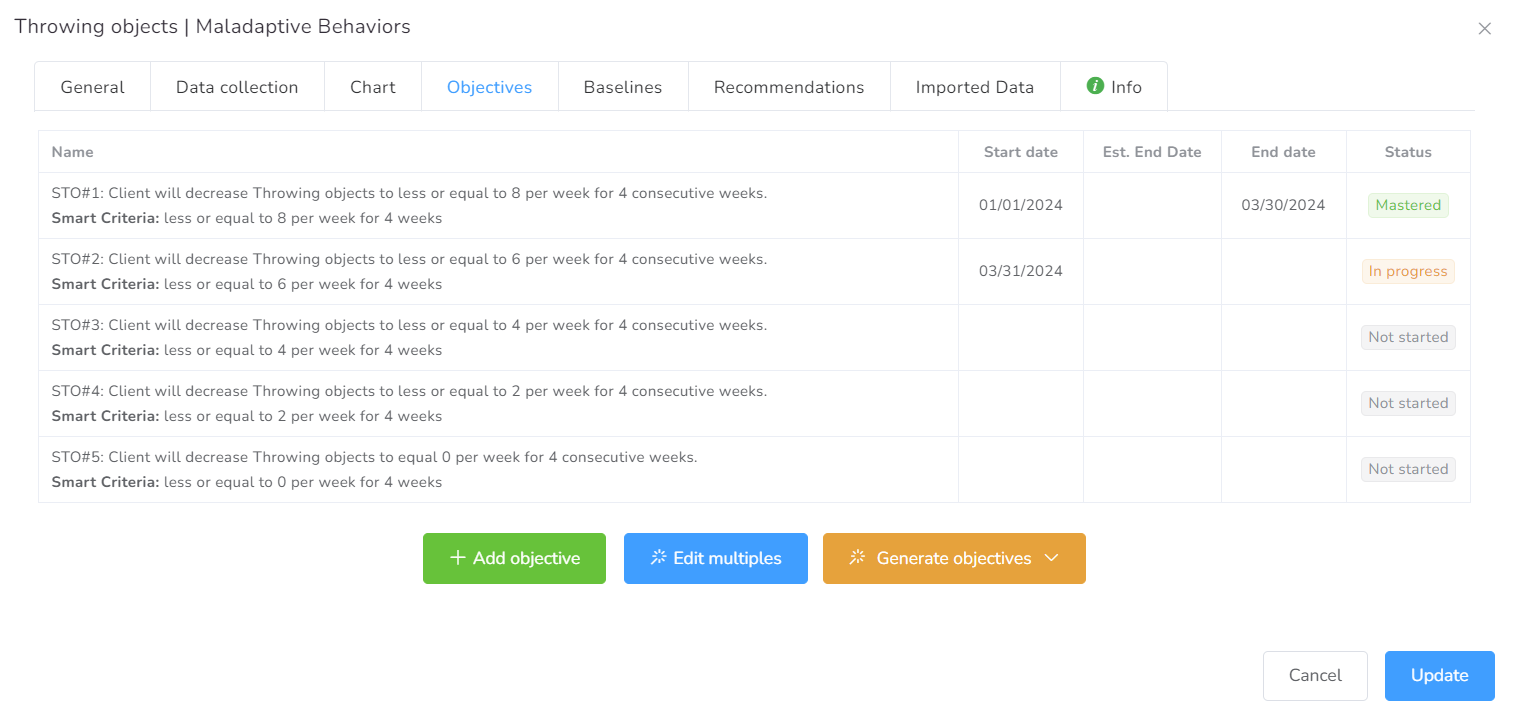
This will set up and track the progress of this element based on the data available in the system. Each objective has a specific configuration that determines how the system will track the objective.
Smart Objective
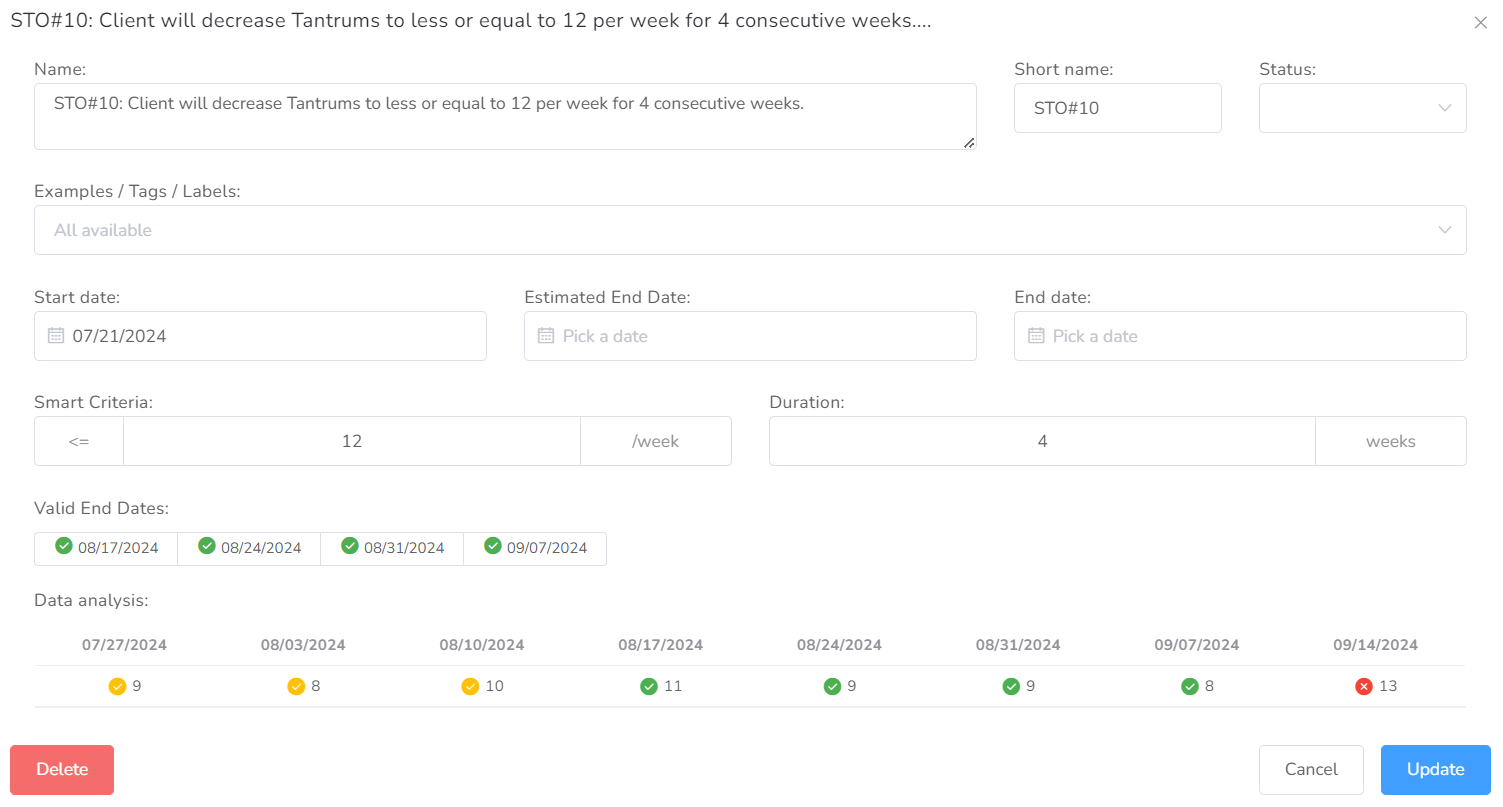
- Name – The name of the objective.
- Short name – A short name of the objective to be shown on the datasheets.
- Start Date – The start date from which this objective will be monitored.
- Estimated End Date – The estimated end date for this objective, on which the target should be mastered.
- End Date – The end date for this objective, after which the next objective in the list will be monitored.
- Smart Criteria – This is the logical representation of the objective, you need to explain in mathematical terms how the objective will be monitored.
- Duration – This is how long the objective lasts until it is met.
- Valid End Dates – If all fields above are completed and there is data collected, the Valid End Date will list all dates considered to be valid. This is used to determine the End Date automatically.
- Data Analysis – This table will represent the data for each interval defined in the Smart Criteria, with different color codes to determine completion.
Now, these STOs will not be updated, change status, or go to Mastered automatically. Our system will only give you a recommendation of the dates on which the STO is met based on the Data inserted, but it is still the BCBA’s responsibility to select a date and have that STO considered mastered.
There are two ways to create Objectives: Add Objectives or Generate Objectives.
- Add Objectives: a box is generated to fill in the fields manually.
How to configure Smart Criteria & Duration
Being a behavior and taking into account the following objective (STO#10: Client will decrease Tantrums to less or equal to 12 per week for 4 consecutive weeks), this is how it should be configured correctly:

- In the first box of Smart Criteria, concerning the sign, select <=.
- In the collected value box, type 12.
- In the time range box, we select /week.
- In the Duration part, in the box for the amount of time, we write 4.
- Lastly, in the time period, we select weeks.
Baselines Tab
You can add all the baselines available by clicking “Add Baseline Button”.
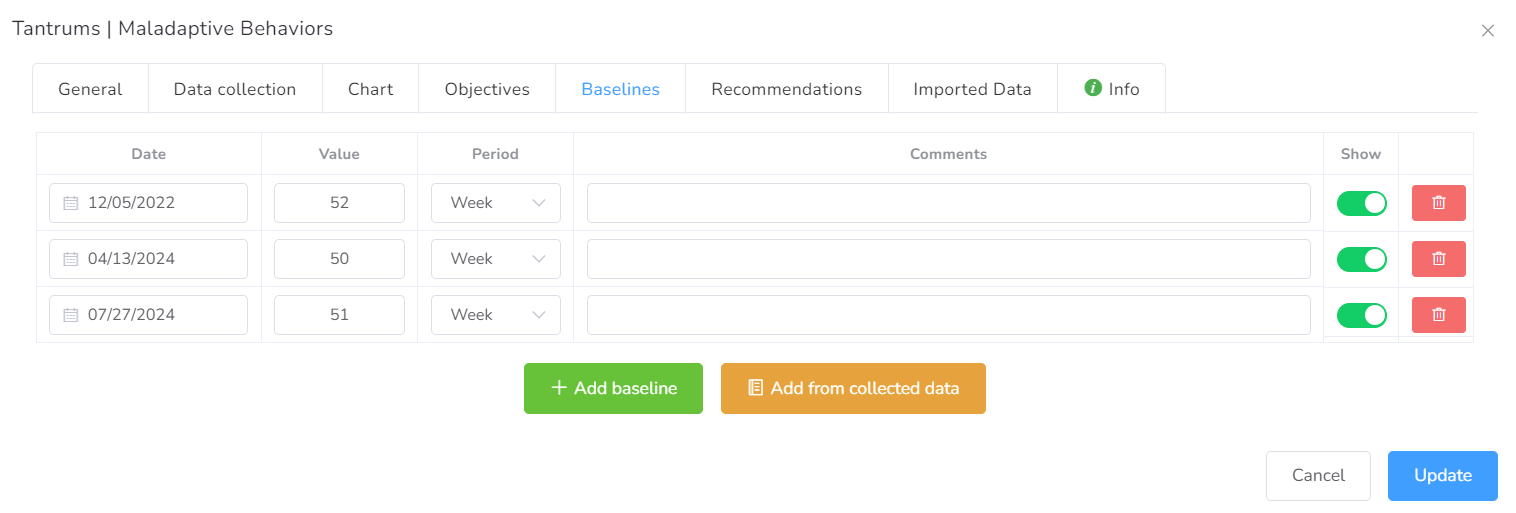
You have two options to add the baseline: adding from scratch or from collected data.
1- Adding baseline from scratch. You need to type the date, and values and choose the period.
- Date – The date associated with this baseline.
- Value – The value for this baseline.
- Period – The period this baseline represents, available options are Day and Week.
2- Adding the baseline from collected data.
Recommendations Tab
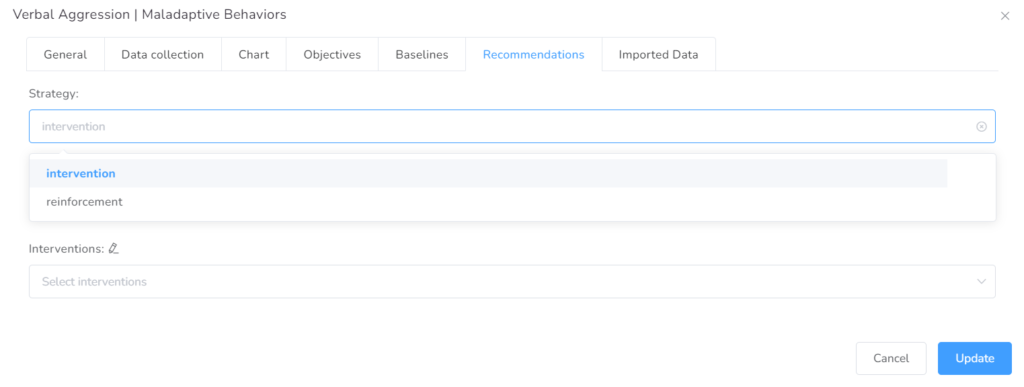
In this tab, you can add the interventions and reinforcers, as well as antecedents and activities implemented prior to occurrence.
By choosing Interventions on the first box, you can select from the dropdown list, the Antecedents prior to ocurrence, or by clicking the pencil next to the name, you can type f there is not you require antecedent.
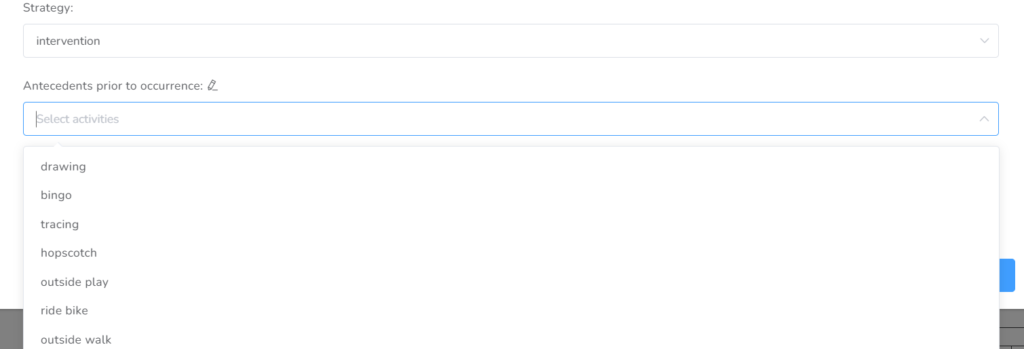
Next, you select the Interventions from the list or add those that are on it.
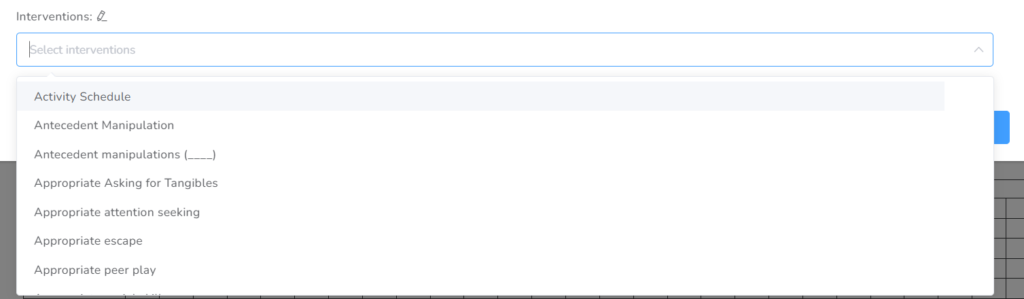
Then you can repeat the steps to add the reinforcers to the Client’s Service Plan.
Imported Data Tab
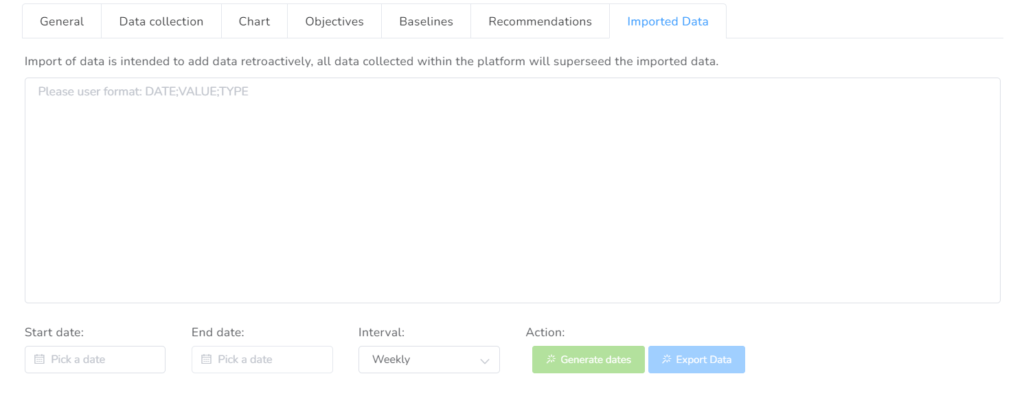
If you have existing data collected outside of Office Puzzle, you can import the data for each element in the service plan by simply converting your data to the format “DATE;VALUE;TYPE”.
DATE
You can put the DATE value in any of the following formats:
- MM/DD/YYYY (Ex: 02/10/2023)
- YYYY-MM-DD (Ex: 2023-02-10)
- YYYY/MM/DD (Ex: 2023/02/10)
VALUE
The value that will be associated with this DATE, this value is expected to be a NUMBER and shouldn’t contain any letters or sign. For example, if your value is 10% the input should be “10”.
You can generate the dates by adding start and end dates. Then you select the interval and hit Generate dates.
 Also, you can import the data, by copying and pasting the dates and values into the box, and clicking on Update.
Also, you can import the data, by copying and pasting the dates and values into the box, and clicking on Update.Export data
On this tab, you can also choose a range of dates in order to export the values of the collected data, if needed.

You just need to select the start and end dates, choose the interval (daily/weekly) and hit the Export data blue icon. This action will download onto your device a CSV file with the chosen information.
